News Center
Dithiocarbamate products, including sodium dimethyldithiocarbamate, potassium dimethyldithiocarbamate, sodium diethyldithiocarbamate, potassium diethyldithiocarbamate, sodium dibenzyldithiocarbamate, etc., all use carbon disulfide in their production processes. Recently, the price of carbon disulfide has been gradually rising since 2024. Especially in the fourth quarter of 2025, with the continuous release of positive market news, the price will continue to rise.


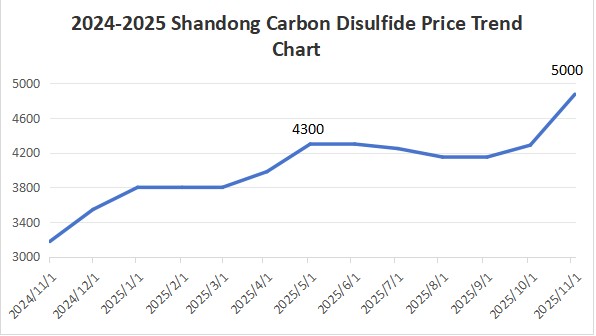
The table above illustrates carbon disulfide's price movement from November 2024 to November 2025, showing a rise from approximately CNY 3,100 to CNY 5,000 alongside emerging supply shortages. Three core factors drive this price surge: surging raw material costs, constrained supply, and growing demand.
I. Surging Raw Material Costs
The main raw materials of carbon disulfide are sulfur and natural gas.
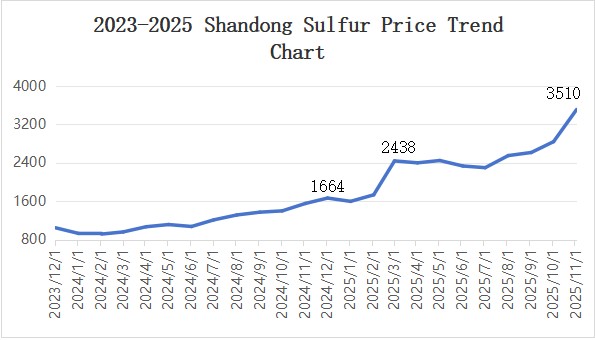
1.1 Sulfur
Sulfur prices have trended upward with fluctuations over the past three years, hitting a three-year high in 2025 with an annual average increase of 84.20%. This rally stems from a confluence of factors: persistent supply constraints, booming demand in the new energy sector, geopolitical tensions, and low inventory levels.
Sulfur demand is concentrated across four key sectors:
l Agriculture (60% of total demand): The largest consumer, primarily for phosphate fertilizer production.
l New Energy (8% of total demand, fast-growing): Sulfuric acid derived from sulfur serves as a raw material for lithium iron phosphate (LFP), with demand in this segment rising sharply.
l Traditional Industry (19% of total demand): Stable consumption for titanium dioxide (12%) and caprolactam (7%) production.
l Other Sectors (18% of total demand): Includes general sulfuric acid production (13%) and environmental applications such as flue gas desulfurization and wastewater treatment (5%).
Demand-supply dynamics further amplify price pressures. Global sulfur supply is projected to reach 8.07 million metric tons in 2025, while demand is expected to hit 8.5 million metric tons—a deficit driven by 3 million metric tons of new demand from Indonesia and 1 million metric tons from China. China's total sulfur demand is forecast to reach 1.52 million metric tons in 2025, with the LFP industrial chain alone boosting industrial-grade monoammonium phosphate output by 36%. Sulfur consumption for LFP production is expected to peak at 177,000 metric tons in 2025, a 55% year-on-year increase.
On the supply side, multiple disruptions have constrained output: Russian refineries cut production by approximately 100,000 metric tons due to Ukrainian attacks, while EU and U.S. sanctions disrupted Russian exports. Meanwhile, traditional Middle Eastern supply has been diverted to Indonesia's nickel smelting projects, reducing shipments to China and other traditional markets. Efforts to secure alternative supply sources have yet to yield tangible results.
With no significant supply growth, surging demand from Indonesia and the LFP sector has created a relative supply crunch.
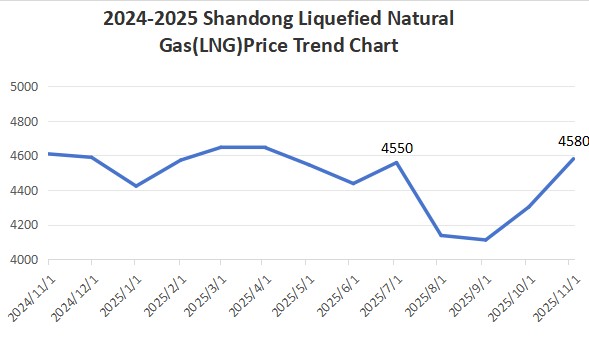
1.2 Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG)
International LNG prices remain elevated, with reduced import volumes pushing up procurement costs. Simultaneously, growing demand from both upstream and downstream sectors has increased liquid plant shipments. Faced with cost pressures, upstream suppliers have proactively raised prices. The onset of the heating season has further boosted natural gas costs, directly increasing carbon disulfide production expenses.
II. Contraction on the Supply Side
Tightened supply has boosted the price of carbon disulfide.
2.1 Concentrated Domestic Maintenance
Domestic carbon disulfide production facilities have undergone concentrated maintenance, creating periodic supply tightness. Capacity utilization has remained around 65% during this period.
2.2 Phase-Out of Outdated Capacity
China's "Dual Carbon" goals (carbon peaking and carbon neutrality) have accelerated the phase-out of outdated, inefficient production capacity, further constraining overall supply.
III. Growing Demand
Demand for carbon disulfide has strengthened across both traditional and emerging downstream sectors, creating a demand-supply imbalance.
3.1 Traditional Industries
Demand from traditional sectors has remained stable, with export growth driving simultaneous increases in both domestic and international consumption.
3.2 Emerging Sectors
Emerging application areas have seen rapid demand growth, further straining available supply.
IV. Dithiocarbamate Products
4.1 2025 Demand Trend
Dithiocarbamate demand has risen significantly in 2025, with global consumption projected to reach 246,000 metric tons—creating a 24,000 metric ton supply gap. This growth is fueled by three key drivers:
1. Steady demand growth in agricultural fungicides;
2. Rapid expansion in industrial applications;
3. Sustained growth in export demand.
4.2 2026 Price Forecast
Multiple positive drivers will likely trigger a price increase cycle for dithiocarbamate products in 2026.
Raw Material Cost Projections
Carbon disulfide prices are expected to exhibit high volatility and regional divergence in 2026. Rigid cost support and an improved demand-supply structure will collectively underpin an overall upward price trend.
Tight Demand-Supply Balance
The global dithiocarbamate market will maintain a tight demand-supply balance in 2026. While supply of traditional pesticides and rubber additives will be sufficient, structural shortages will persist for high-purity and environmentally friendly specialty products—requiring technological upgrades and imports to fill the gap.
Against this backdrop, dithiocarbamate price increases in 2026 are inevitable, driven by rising raw material costs and tight demand-supply dynamics. Furthermore, due to structural shortages, high-end products (high-purity and environmentally friendly variants) will see significantly larger price hikes than traditional products.
This analysis is based on current available information and is for reference only. We welcome feedback for continuous refinement in practical application.
